Source: Pinterest
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment in which patients breathe pure oxygen in a pressured setting, usually a hyperbaric chamber. This treatment method has gained popularity due to its potential advantages in a variety of medical diseases, including healing wounds, decompression sickness, and radiation damage.
HBOT increases oxygen flow to tissues and aids healing processes by providing oxygen at higher-than-normal atmospheric pressure. The proper number of HBOT treatments, on the other hand, is critical for increasing its effectiveness and guaranteeing patient safety.
Understanding the suggested frequency enables healthcare practitioners in developing suitable treatment regimens that take into account elements such as the ailment being treated, unique patient response, and potential adverse effects. Exploring the optimal number of HBOT sessions is therefore critical for maximizing treatment results and delivering the best possible care.
The Science Behind HBOT

Source: Pinterest
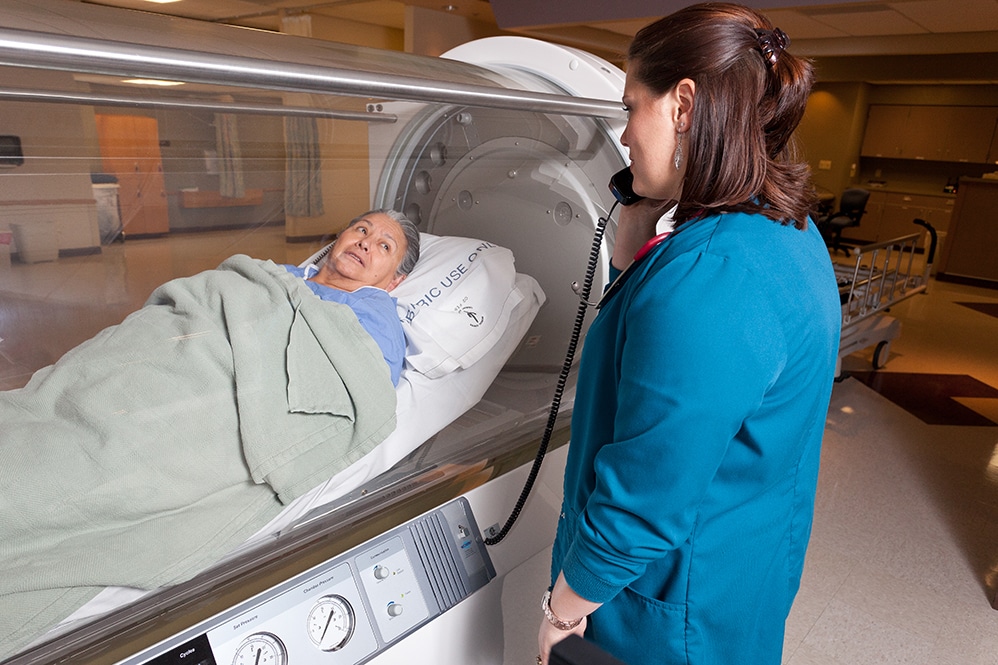
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) exerts various physiological effects on the body. For a patient to receive HBOT, the patient is positioned inside a hyperbaric chamber where the individual breathes using pure oxygen under higher atmospheric pressure. The procedure employs numerous treatment mechanisms.
To begin with, the elevated pressure facilitates an increased level of oxygen to disintegrate inside the vascular system. Thus, increased oxygen transport to the body’s cells. Air is essential for cellular metabolic processes and contributes an important role in the recovery from wounds, the repairing of tissues, and battling infections.
The increased oxygen levels attained during HBOT stimulate the generation of new blood capillaries. This method is called neovascularization. This assists in providing oxygen and sustenance to zones with reduced blood flow. Furthermore, The application of HBOT stimulates the production of growth factors and regenerative cells. These elements and organisms additionally contribute to the regeneration of tissues and healing.
Oxygen therapy in a pressurized chamber has demonstrated effectiveness in different medical ailments. To illustrate, it is regularly utilized to accelerate wound healing. Especially in instances concerning ulcers that occur on diabetic patients’ feet, wounds from surgery that fail to heal, including instances of severe burn wounds. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is used in radiation-induced injuries, including injury to tissues caused by radiation caused by the management of cancer. This has further demonstrated a likelihood of success in dealing with specific brain disorders.
Including CO exposure, severe head trauma, and cerebrovascular accident.
In general, The capability of HBOT to increase oxygen levels within the body presents a wide variety of medical benefits. This makes it a useful medical alternative for different ailments in which impaired tissue healing, oxygenation deficits, and neurological dysfunction are present.
Factors Influencing HBOT Frequency
Individual Health and Medical Condition
Source: Pinterest
The frequency of hyperbaric oxygen treatment (HBOT) sessions is advised based on a number of criteria, including the individual’s health and medical condition. The severity of the ailment is frequently a factor in selecting the frequency of therapy. A higher frequency of HBOT treatments may be advised in more severe situations if there is considerable tissue damage or a larger requirement for tissue regeneration. This enables more constant and continuous exposure to the therapeutic benefits of higher oxygen levels.
Certain medical issues may demand more frequent HBOT sessions as well. Chronic non-healing lesions, such as diabetic foot ulcers or radiation-induced tissue damage, for example, may require HBOT treatments to enhance recovery. These disorders, which often entail poor tissue oxygenation and limited blood flow, can benefit from HBOT’s increased oxygen supply and angiogenesis-promoting effects.
The severity and acute nature of some neurological illnesses, such as traumatic brain damage or carbon monoxide poisoning, may necessitate more frequent HBOT treatments at first. This aggressive treatment strategy attempts to minimize immediate harm and promote early healing.
It should be noted that the recommended frequency of HBOT is chosen on an individual basis and is adjusted to each patient’s particular demands and responses. In consultation with the patient, the healthcare professional evaluates numerous criteria such as the patient’s general health status, underlying medical disorders, treatment objectives, and tolerance to HBOT.
Treatment Goals
Source: Pinterest
The number of hyperbaric oxygen treatment (HBOT) sessions is determined by the therapeutic goals associated with a certain condition. It is crucial to distinguish between acute and chronic disorders when determining treatment time and frequency.
Acute diseases, such as carbon monoxide poisoning or decompression sickness, may need immediate and substantial HBOT to address the immediate repercussions while limiting long-term implications. HBOT treatments may be administered more often in certain conditions, typically in a series of sessions over a short period of time.
Chronic ailments, on the other hand, such as non-healing wounds, radiation damage, or some neurological issues, may necessitate a lengthier treatment duration. In these cases, the recommended frequency of HBOT treatments can be spread out over a longer period of time, allowing for progressive and consistent improvement.
HBOT treatment objectives should be defined in conjunction with a healthcare professional who is knowledgeable about hyperbaric medicine. They will assess the patient’s specific disease, medical history, and personal circumstances to identify appropriate therapeutic goals. The intended objectives, the probability of tissue repair or functional improvement, and the patient’s reaction to HBOT are all factors considered by the healthcare practitioner.
Working with a healthcare expert is vital since they have the knowledge to tailor the treatment plan to the individual’s needs. They can monitor progress, adjust the amount of HBOT treatments as needed, and determine whether therapeutic goals are being met.
HBOT Protocols and Guidelines

Source: Pinterest
The frequency of sessions in hyperbaric oxygen treatment (HBOT) is guided by recognized procedures. The protocols used may differ depending on the medical condition being treated and the instructions supplied by medical authorities.
A conventional HBOT protocol generally consists of a series of treatments ranging from 20 to 60 sessions, depending on the condition and response to therapy. These lessons are frequently given daily or several times per week. Each session normally lasts 60 to 120 minutes, during which the patient breaths pure oxygen at high atmospheric pressure within a hyperbaric chamber.
Guidelines for the appropriate use of HBOT are provided by medical authorities such as the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society (UHMS).These guidelines define the situations for which HBOT is thought to be useful, as well as recommendations for treatment frequency and duration.
For example, the UHMS has developed particular standards for carbon monoxide poisoning, decompression sickness, and non-healing wounds. These suggestions may include the number of sessions, the pressure employed, and the frequency of treatments.
Furthermore, based on their experience and competence in hyperbaric medicine, each medical institutions and healthcare practitioners may have their own procedures. When setting the number of HBOT sessions, they may take into account aspects such as patient reaction, severity of the illness, and intended therapeutic goals.
It should be noted that following established rules and recommendations assures the safe and successful use of HBOT.
Consultation with Medical Professionals

Source: Pinterest
When considering hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), it is necessary to consult with a trained healthcare provider. They are crucial in determining the amount of HBOT treatments that are appropriate for you depending on your unique medical condition, treatment goals, and individual response.
Medical professionals, such as hyperbaric medicine experts or wound care specialists, may examine your condition and advise you on the best treatment plan for you. They will evaluate the severity of your ailment, your medical history, and any potential risks or contraindications.
You may find reputable HBOT clinics and healthcare professionals by:
- Seek referrals: For ideas, go to your primary care physician or a specialist. They may be aware of reputable HBOT clinics or physicians in your area.
- Examine credentials: Look for board-certified hyperbaric medicine practitioners or those with particular training and skill in HBOT. Examine their credentials, affiliations, and areas of expertise.
- Examine the following testimonies and reviews: Look for reviews and testimonials from patients who have received HBOT from certain centers or specialists. Their experiences might disclose details regarding the quality of care provided.
- Make that the HBOT center is recognized by a respected organization, such as the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society (UHMS) or another analogous certifying authority.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Frequency
It is critical to monitor the progress of patients during hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) in order to optimize treatment outcomes. Regular evaluation allows healthcare experts to examine the success of the treatment and change the number of HBOT treatments as needed.
Based on continuing evaluations, healthcare providers can examine the treatment plan and determine if the current number of HBOT sessions is enough or whether changes are needed. This may imply raising the frequency for disorders that require more extensive therapy or reducing the frequency for ailments that have achieved great progress.
The objective is to keep the treatment personalized to the patient’s unique demands while also maximizing the possible advantages of HBOT.
Conclusion
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) requires personalized treatment strategies and physician monitoring. It is critical to consult with healthcare providers to identify the best frequency of HBOT treatments based on individual needs.
Patients can assure safe and successful therapy by obtaining professional advice, maximizing the potential advantages of HBOT for their unique ailments.